Glassy Carbon

We are dealing with various kinds of Glassy Carbon products. Customer's special processing order such as pipe, pot shape etc. or custom sizing order is also available.
| Catalog No. | Description | Size |
| ROD | ||
| 010761 | R-1 Glassy Carbon rod | OD 1.0x100 mm |
| 010762 | R-2 Glassy Carbon rod | OD 2.0x100 mm |
| 010763 | R-3 Glassy Carbon rod | OD 3.0x100 mm |
| PLATE | ||
| 012086 | P-1 Glassy Carbon plate | 1.0x25x25 mm |
| 012087 | P-2 Glassy Carbon plate | 2.0x25x25 mm |
| 012088 | P-3 Glassy Carbon plate | 3.0x25x25 mm |
| FILM | ||
| 012089 | F-1 Glassy Carbon film | 0.1x25x25 mm |
| POWDER | ||
| 012090 | S-12 Glassy Carbon powder (Spherical) | 0.4-12 µm, 10 g |
| 012091 | S-20 Glassy Carbon powder (Spherical) | 10-20 µm, 10 g |
| 012092 | S-50 Glassy Carbon powder (Spherical) | 20-50 µm, 10 g |
| 012093 | S-80 Glassy Carbon powder (Spherical) | 40-80 µm, 10 g |
| 012094 | S-200 Glassy Carbon powder (Spherical) | 80-200 µm, 10 g |
Features of Glassy Carbon
- High-purity
- Excellent Stability as high as at 3,000 °C in vacuum / at 500 °C in the air
- Well Inert against Chemical erosion
- Impermeability to Gas and Solution
- Significant Hardness / Strength
- Brings Fine surface condition after polishing
- Favorable electric conducting property
- Dielectric characteristics in High-frequency
- Highly Resistant against Inorganic and Organic salts
- Good Bio-Compatibility
- Isotropic Physical/Chemical properties
Glassy Carbon - Physical Property
| Density | 1.42 g/cm3 |
| Upper Temparature Limit in vacuum | 3,000 °C |
| Porosity | 0% |
| Gas Transmission Rate | 10-9 cm3/s |
| Hardness | 230 HVI |
| Bending Strength | 260 N/mm2 |
| Compressive Strength | 480 N/mm2 |
| Young's Modulus | 35 kN/mm2 |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient (20-200 °C) | 2.6 x 10-6 1/K |
| Heat Conducting (@30 °C) | 6.3 W/(K•m) |
What is Glassy Carbon?
Glassy Carbon has quite unique structure. As the figure below shows, this material contains random combination of basal plane and edge plane.
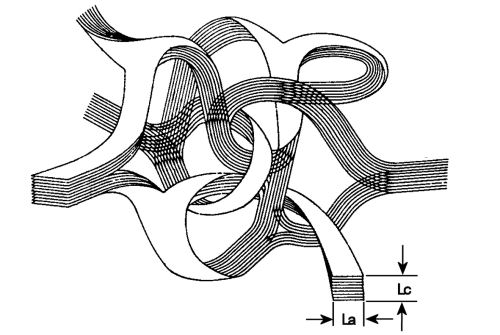
La: Intraplanar Microcrystaline Size, Lc: Interplanar Microcrystaline Size
(G.M. Jenkins and K. Kawamura: Nature 231,175 (1971).)